1973 - The rise of FM & NWC 1000kW VLF Transmitter Activated!
FM radio was an innovation that modulated the frequency instead of the amplitude patented by Edwin H. Armstrong in 1933. This reduced static, electrical equipment, and atmospheric interference.
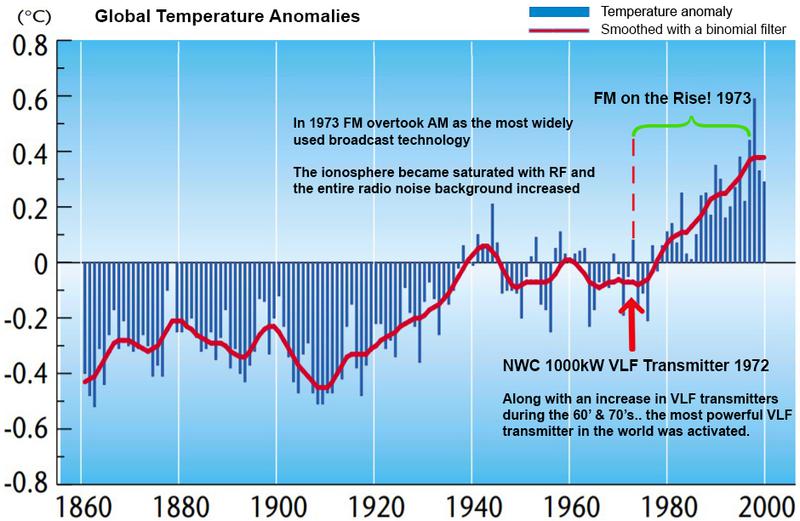
Despite FM being developed in the 40’s, it took a long time for it to be adopted by the majority of radio listeners. Early on it was primarily used to broadcast classical music in urban areas, and educational programming. By the late 1960s FM had been adopted by fans of “alternative rock” music brought on earlier by the rise of such stars as Buddy Holly and many others that ushered in a new era of rock. It wasn’t until the mid 70’s that FM became mainstream and overtook AM broadcast radio. (see Figure 13)
[Figure 13: As FM was on the rise and the most powerful VLF transmitter in the world was activated in the 70’s the entire radio noise background and global temperature began to rise.]
In 1972 before the rise in FM broadcasting, the NWC VLF Transmitter in Australia was activated. It’s the most influential VLF transmitter on magnetospheric particle activity, and when it was turned on there was also a sudden rise in the entire background of radio noise AND in global temperature.
“Another space-based RF survey at 1.0–5.6 MHz measured from 100,000 to 120,000 km above Earth found evidence of increasing man-made terrestrial radio background between 1973 and 1988. In our case we have found no statistically significant change over the review period of November 1997 to December 1999.” ..ie. 1998
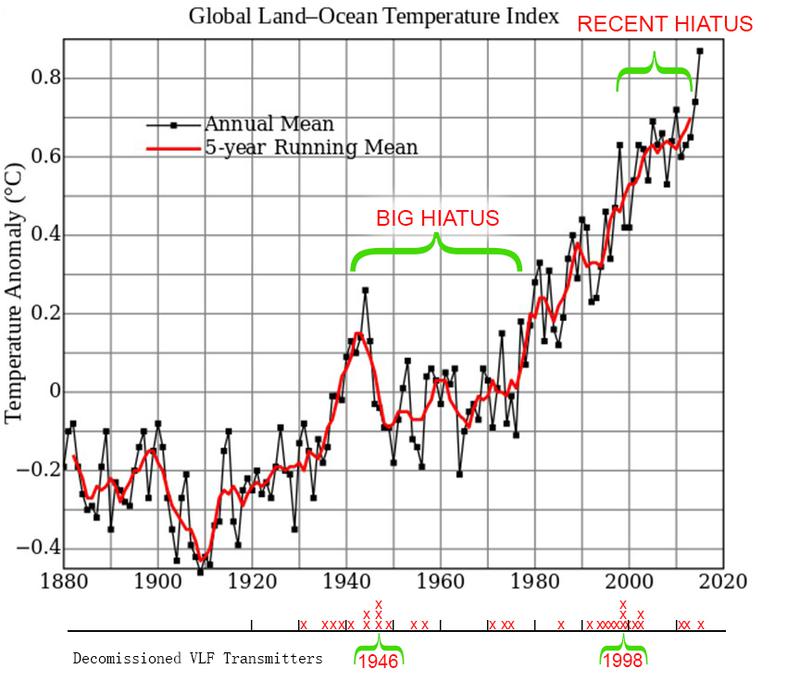
If you do a histogram of decommissioned VLF Transmitters you’ll find two years had more high powered VLF transmitting stations taken down; 1946 and 1998.. both years also saw arguably significant decreases in global temperatures. The Great Winter of 1946/47 was renowned as the coldest winter in 50 years. 1998 was known to some as the ‘Global Warming Hiatus’, which is argued as a
significant changing point in the mainstream ‘Global Warming’ narrative. (see Figure 14)
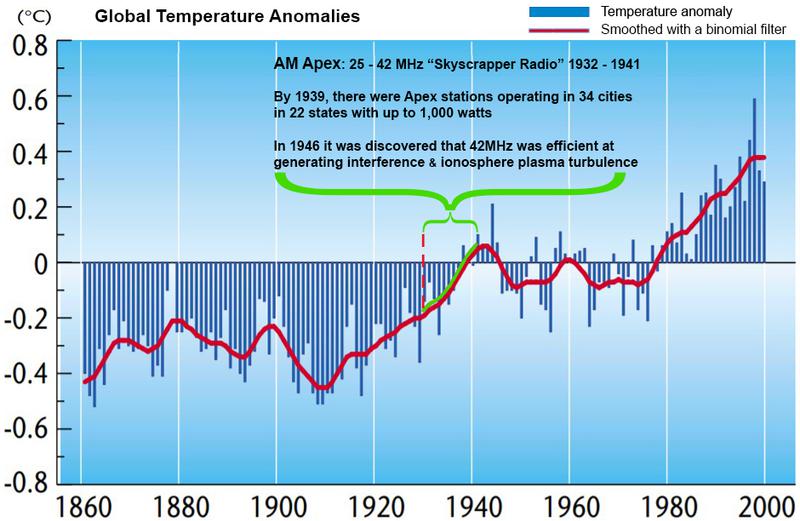
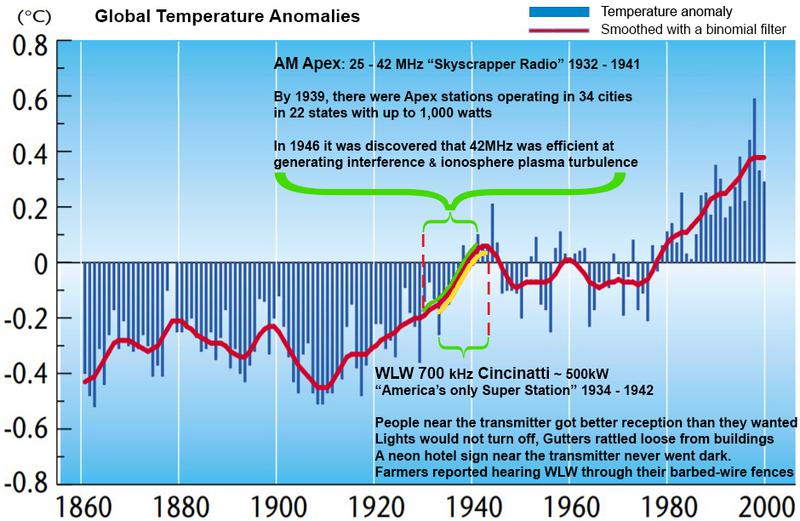
[Figure 11: The frequency of AM Apex (42MHz) was found to be efficient at causing interference and ionospheric turbulence. When Apex broadcasting ceased, the global temperature stopped rising.]
One of the questions Broadcast Theory asks is; could it be possible the discontinuation of Apex stopped stimulating ionospheric turbulence and upper atmospheric EEP-NOx ozone depletion processes?
1934 - Station WLW-700 The world first AM Superstation!
To understand the sheer power of a radio station’s effect on its local environment
one need look no further than WLW 700 Cincinnati. For a brief time in the 1930s,
radio station WLW in Ohio became America’s one and only AM radio “Super Station”!
(see Figure 12)
In 1934, when President Franklin Roosevelt pushed a ceremonial button on his desk,
a five hundred thousand-watt (500 kW) behemoth stirred outside Cincinnati. Rows of
five-foot glass tubes warmed and water flowed around them at more than six hundred
gallons per minute. Dozens of engineers lit filaments and flipped switches, and, within
the hour, enough power to supply a town of one hundred thousand coursed through an
831-foot tower and WLW had the ability to reach most of the country.
“People living near the transmitter site often got better reception than they wanted;
some lights would not turn off until WLW engineers helped rewire houses. Gutters
rattled loose from buildings. A neon hotel sign near the transmitter never went dark.
Farmers reported hearing WLW through their barbed-wire fences."
Because of the incredible power WLW held over the airwaves, its ability to broadcast
at 500kW was reduced in 1939 and terminated in 1942.
Station WLW700 operated at 500,ooo watts within the gyro-frequency range which as
discussed could boost passing VLF signals 4 - 10 times using only 400/500 watts.
500,000 watts is 1000 times the needed power to stimulate the Bailey Effect and if the
equation was linear would result in a 4000 - 10,000 times increase in regional
VLF signals!
Radiation Belt Remediation
The idea that VLF Transmitters can affect upper atmospheric chemistry and weather isn’t new. In a research paper from 1977 called, “VLF Transmitter Induced Slot Electron Precipitation”, Vampola et.al. it was hypothesized the energy input into the upper atmosphere in the vicinity of such transmitters may have a measurable effect on the weather.
Interestingly, it was also stated that if we stopped radiating VLF at high powers, it’s likely the radiation belts would fill in and become too energetically hostile, damaging satellites causing them to fall out of orbit. And furthermore, how we might use VLF to intentionally modify the radiation belt particle population.
In 2017, the Air Force launched the DSX satellite aboard the SpaceX Heavy Falcon2 rocket with plans to test a satellite-based VLF transmitter for intentionally altering the radiation belt particle population in what’s become the largest geoengineering scheme in the world, called ‘Radiation Belt Remediation’. Experimentally, the VLF transmitter may drain the radiation belt of harmful radiation, mitigating damage to orbiting satellites in case of nuclear attack or “natural” build up. So the VLF-driven EEP is important to understand as a matter of National Security.
In December of 2019 Science magazine came out with an article on Radiation Belt Remediation saying these experiments may spawn heaps of nitrogen oxides and hydrogen oxides, which could eat away at the stratospheric ozone layer. In the article Dr. Allison Jaynes states that, “We don’t know how great the effect would be” on our atmosphere.
In a recent paper exploring the impacts of space weather on the habitability of terrestrial-type exoplanetary climates, Energetic Electron Precipitation induced variations in mesospheric ozone (up to 34%) is shown to have possible long term impacts on climate. They say the IPCC has recognized the potential significance of Energetic Electron Precipitation and will include detailed EEP-ozone ion chemistry in their next assessment report in 2022.
Though the global significance of Energetic Electron Precipitation is still uncertain, if we are to have a comprehensive approach to understanding our climate system - even at a regional level - the effects of EEP must be included, especially if it represents of yet another anthropogenic effect on climate and ecology during what many are calling the Anthropocene era.
Not only are humans increasing Greenhouse Gases, but now we’re discovering we may also be influencing the amount of solar UV heating those GHGs via ozone depletion as early as the 1920’s, if not even earlier.
VLF transmitter-induced bubble has been acknowledged as blocking solar particles and potentially affecting the amount of ozone and solar UV entering deeper into the climate system. If we don’t include these anthropogenic variables and dismiss their potential significance, then our equation of the climate system is incomplete. We can’t afford to base our conclusions on an incomplete equation, as it would be irresponsible to act on incomplete understanding, regardless of whether these variables are significant to our environment.
Thus far, the scientific literature doesn’t directly have a name for this hypothetical anthropogenic transmitter induced ozone depletion mechanism. Because of this it gets lost in the discussion and is quite difficult to search for as a topic. You can find tons of research on TIPER; Transmitter Induced Precipitation of Electron Radiation, and you can find tons of research on EEP-NOx; Energetic Electron Precipitation - Nitric Oxide, which is typically considered a solar variable, but there’s little research on how these two interplay - even though this hypothesis was postulated as early as the 70’s and continues to be explored with cutting edge experiments in Radiation Belt Remediation.
TIPER-NOx would be the technical combination of the two and for the rest of this article I will use TIPER-NOx interchangeably with Transmitter Induced Ozone Depletion. Again, this is a hypothesis, but if we’re going to discuss this as a concept, it has to have a name.
What is Broadcast Theory?
So far we’ve looked directly at the mechanism of Transmitter Induced Ozone Depletion aka: TIPER-NOx. Broadcast Theory cross references our historic use of early broadcast frequencies with modern research on how those frequencies interact with ionospheric-magnetospheric dynamics along with global temperature trends to show how the rise in broadcast technology and TIPER-NOx may have contributed to a rise in global temperatures called the Early Twentieth Century Warming (ETCW) period which coincided with our first use of regular global broadcast in 1910 and ended in 1945 with the great winter of 1946/47. And potentially, the global temperature increase that began in the early 70's, which also witnessed a measurable rise in the entire background noise from radio transmitter waves - both trends that stalled briefly in 1998.
By the time FM radio overtook AM and the global use of radar technology had increased in the 70’s, the ionosphere was saturated with technical frequencies from a variety of sources. This and so many other potential variables make it hard to pin trends of the frequencies or transmitters used on specific atmospheric trends or climate dynamics. Because of this the early days of radio are a unique window into the past and how those frequencies may have interacted with ionospheric dynamics that played a role in TIPER-NOx and ozone depletion. Not only did early radio have a profound impact on our understanding of global interconnection, but there was a lot of early research into the nature of radio wave propagation and ionospheric dynamics that has its own exciting story of discovery.
When I first noticed how historic anomalies in global temperature coincided with historic shifts in our use of broadcast frequencies, I had no idea there really was an actual mechanism by which those correlations might be possible. It was only through further investigation I learned about the hypothesis of TIPER-NOx and how some of the world's leading physicists had already pointed it out with concern.
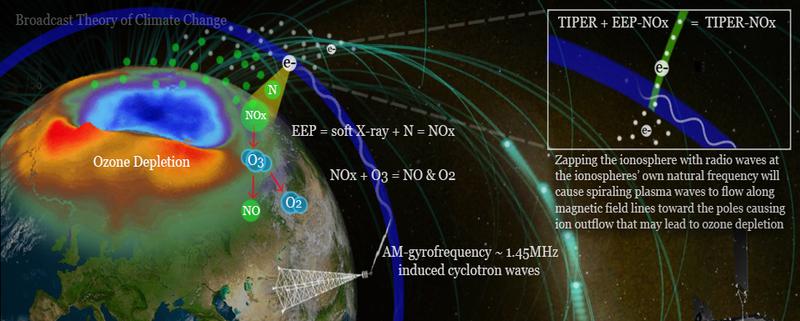
It wasn't until I discovered experiments done using the infamous H.A.A.R.P scientific transmitter in Alaska that I realized radio waves could affect atmospheric chemistry. Through experiments it was discovered that zapping the ionosphere with radio waves using certain frequencies caused spiraling plasma waves called cyclotron waves that flow along Earth’s magnetic field lines toward the poles where it increases ion outflows from the ionosphere and particle densities across the polar cap region.
Another earlier experiment conducted in 1986 called MINIX (Magnetosphere Ionosphere Nonlinear Interaction eXperiment) connected the same shifts in atmospheric chemistry demonstrated using H.A.A.R.P with our use of broadcast frequencies.
They found that if you zap the ionosphere with its own natural frequency, which at 90km is around 1.5MHz, it's super efficient at generating cyclotron plasma waves that travel to the poles fueling ion outflows and shifts in particle densities of the polar cap region. This frequency happens to be in the AM broadcast band and is known as the gyro-frequency. (see Figure 8)
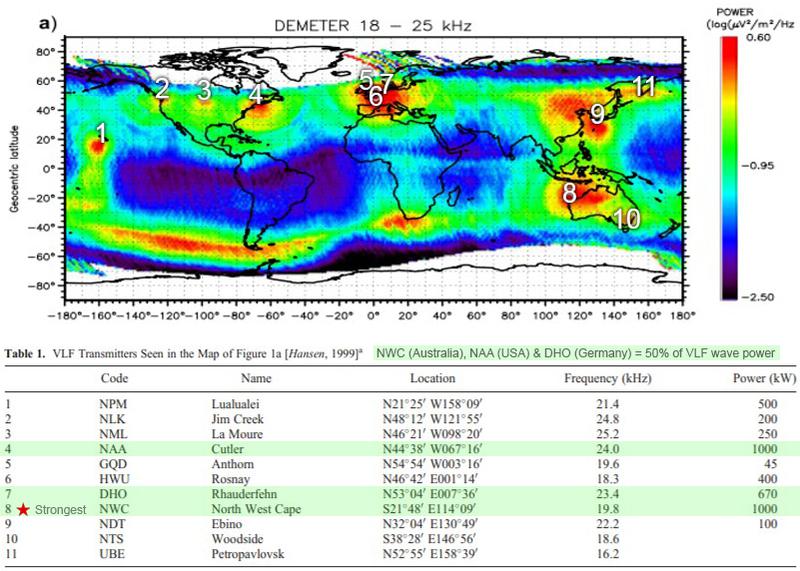
[Figure 3] Higher powered VLF transmitters located around the globe, three of which make up 50% of the total VLF wave power that dominate the wave particle interactions of the inner magnetosphere; NWC - Australia, NAA - USA & DHO - Germany]
The most powerful of these high powered VLF transmitters is the 1000kW NWC Transmitter on 19.8kHz located in Western Australia on the North West Cape near Exmouth. It was activated in 1972 featuring thirteen transmitting towers the tallest of which is 387 metres (1,270 feet) tall. For many years it was the tallest man-made structure in the Southern Hemisphere. Its location close to the equator and low frequency makes it more effective at altering magnetospheric particle populations than any other VLF transmitter.
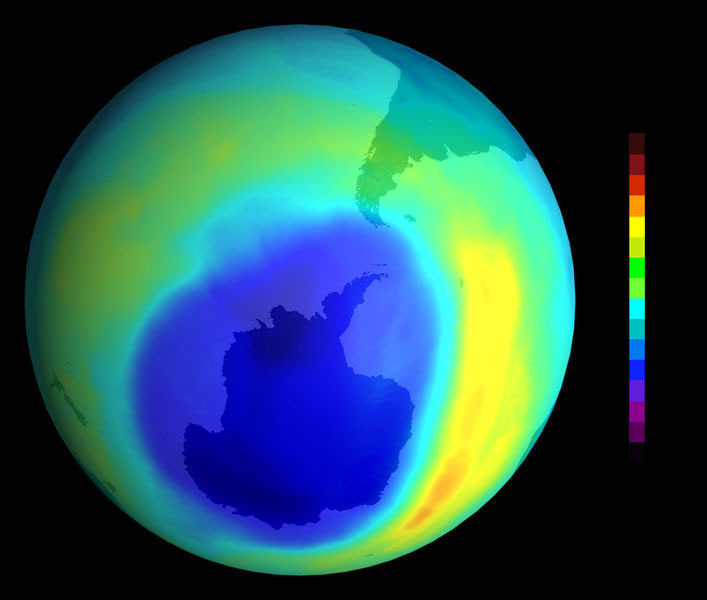
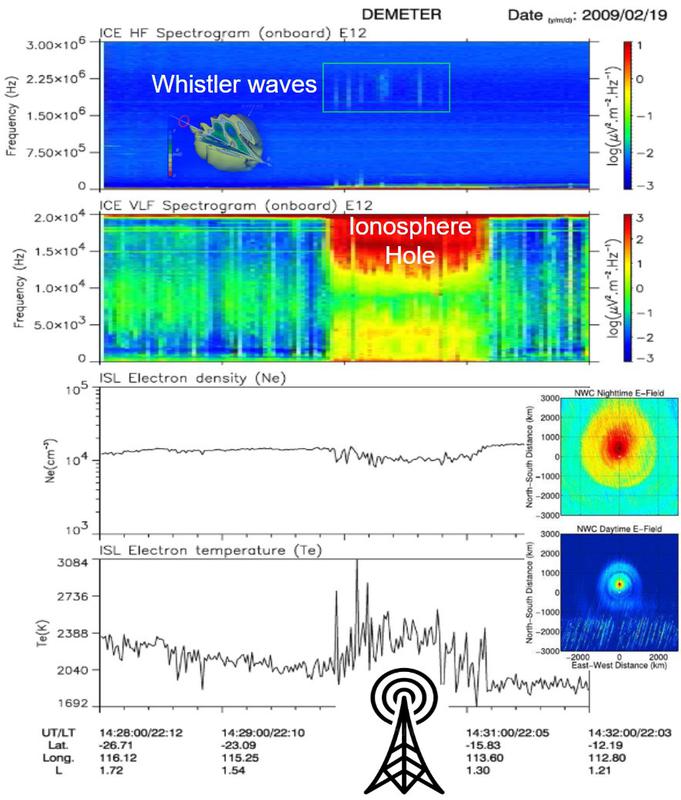
90km above the NWC - VLF Transmitter a 25km ‘hole’ forms in the ionosphere.
This allows higher frequency whistler mode waves and signals from lightning
and other man-made sources to escape the Earth - Ionosphere wave~guide
into the upper atmosphere, fueling changes in upper atmospheric chemistry.
(see Figure 4)
These higher frequency whistler mode waves are observed escaping through
these holes into the atmosphere above these higher powered VLF transmitters.
In fact one paper showed 16 different transmitters had over 258,000 watts of
broadcast energy escaping at night into the upper magnetosphere.
Normally, electrons trapped between the North and South poles of the
magnetosphere hit the ionosphere and bounce back since the magnetic field
of the ionosphere is perpendicular to the magnetosphere.. But transmitter
induced whistler plasma waves knock loose electrons trapped in the
magnetosphere causing them to slide down the magnetic field lines in batches
and rain down onto the ionosphere.
This electron rain is known as Energetic Electron Precipitation.. or EEP-NOx.
Transmitters also create spiraling plasma waves that disturb the ionospheres’
magnetic field so it’s no longer perpendicular to the magnetosphere. These
energetic electrons are then able to slip through the ionosphere and into the
upper atmosphere where they are slowed resulting in a soft X-ray radiation
called bremsstrahlung, or “breaking radiation”.
This radiation is strong enough to react with stratospheric Nitrogen forming Nitrogen Oxides (NOx).
These reactive Nitrogen Oxides (NOx) descend into the polar vortex where it breaks Ozone (O3) down into NO and O2. NOx is really important because most of the global ozone is in the middle stratosphere where the NOx-induced ozone loss is largest.
So although radio waves aren’t strong enough to create NOx or deplete ozone directly, they do cause spiraling waves in the ionospheric plasma and allow magnetospheric electrons to rain down in batches upon the upper atmosphere with enough energy to affect NOx and ozone. (see Figure 5)
[Figure 5: Magnetic field, ionosphere and EEP-NOx, possibly leading to the depletion of ozone.]
Dr. Allison Jaynes spoke on Cutting Edge Radiation Belt Research at the 2018 National Academy of Sciences stating that “if energetic enough”, precipitating electrons could have long term impacts on weather and climate via ozone variation.
~ Broadcast Theory of Climate Change ~
Transmitter Induced Ozone Depletion in the Early Twentieth Century Warming period:
Climate Change is one of the most polarizing issues of our time, to some it’s not real and all a political plot to redistribute wealth, while others are seeing the ecosystem and their world change around them at a rate they’ve never known before. Some see a consensus within the scientific community while other scientists are not yet convinced that we fully understand the whole picture.
When my journey with Broadcast Theory began, I was researching CO2-driven climate change for a website to help bring people together, find solutions and create real change in the world. I was new to the topic, moved by the implications it had on generations to come and had no reason to doubt its validity. However as I began to research I learned more of a great debate that raged on. The idea of a consensus on the issue had only just begun so I was baffled to see how many scientists were still struggling with the information that was being presented as fact and proof with regards to a climate system too large to prove anything. But could anybody completely deny that our climate was changing more rapidly than ever?
Looking deeper I found some of the arguments against CO2-driven Climate Change to be too good to ignore, but still wondered if there was something amiss in our complex climate system as there were still many unanswered questions - such as the cause of the Early Twentieth Century Warming (ETCW) between 1910 - 1945 with a temperature increase of 0.37 K between 1925 - 1944. Even scientists in line with the official stance of the IPCC acknowledge that there simply wasn’t enough CO2 in the atmosphere for it to be the leading climate forcing mechanism. Could there be something else affecting our atmosphere that fits our global temperature anomalies? This question haunted me, so in a process to understand it all, I sought an approach from an unbiased perspective beyond the alarmist/denier binary: to learn the pros and cons of every theory I could find and come up with a clear idea of what was really going on. While researching I came across something strange: The temperature anomalies of the modern age seemed to correlate with the expansion of the global broadcast network.
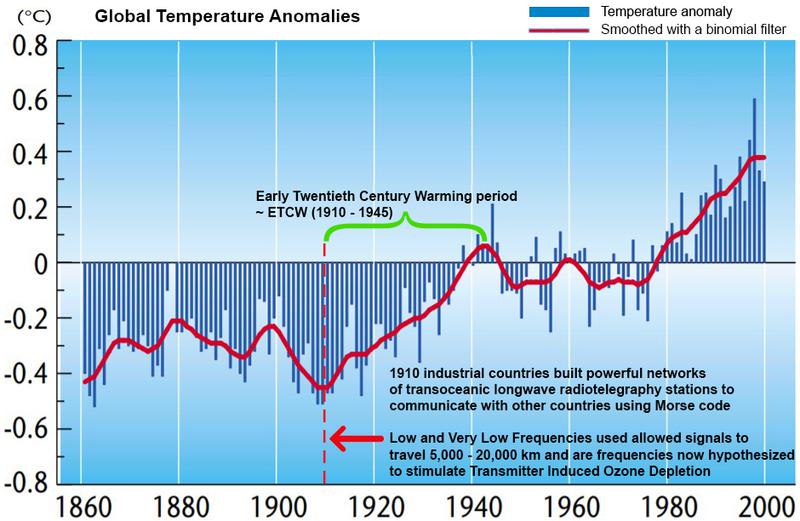
The global temperature anomalies graph from the World Meteorological Organization (see Figure 1) shows that Global Warming started around 1910, the beginning of the Early Twentieth Century Warming (ETCW) period. This also happens to be when industrial countries built powerful networks of broadcast stations.
Broadcast Theory of Climate Change
for a more in depth look see:
TIPER-NOx: Transmitter Induced Ozone Depletion ~ in a nutshell
Research Sections
for latest news on EEP-NOx see:
Learn More
A Revolutionary Perspective on Climate Change
2007 ~ 2021
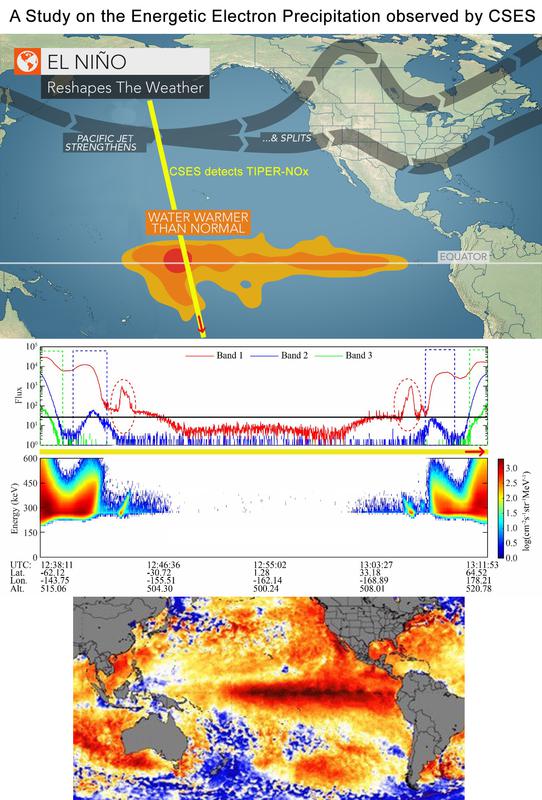
[Figure 7: CSES satellite detects a region of enhanced Medium energy EEP over a warmer than normal region of water in the Pacific Ocean significant in wind and sea temperatures of tropic/subtropical climates]
[Figure 6: A long term EEP-NOx trend that doesn’t match solar and geomagnetic activity may be from VLF transmitters]
Broadcast Theory and the Sun ~ Anthropogenic Solar Activity?
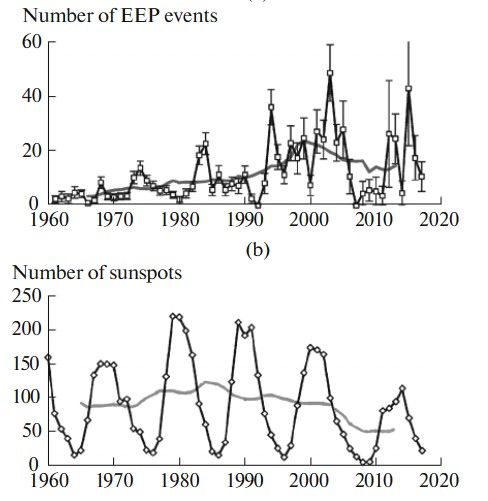
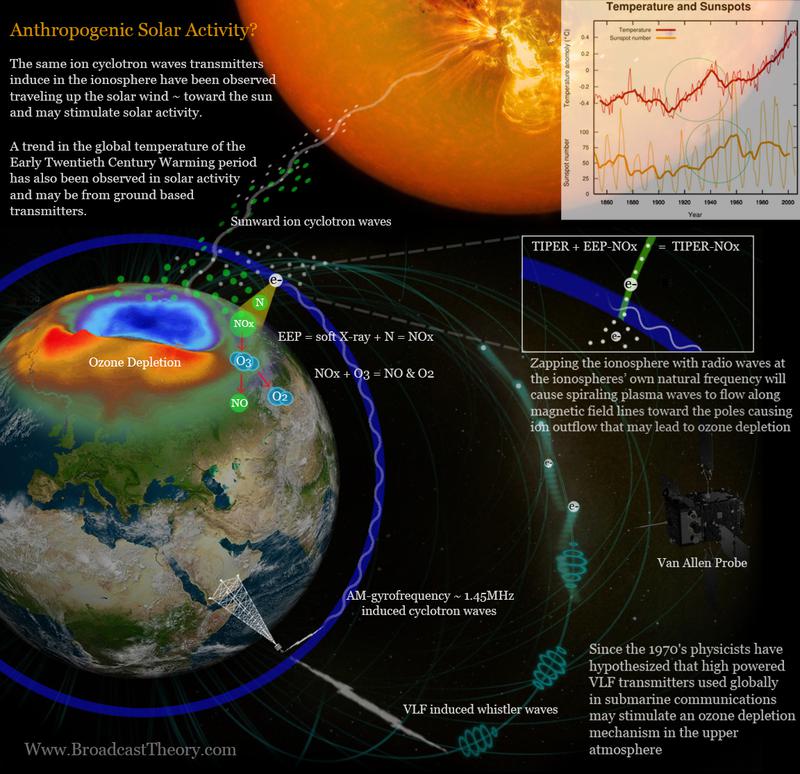
In 2014, a research paper came out with analysis of 13 solar cycles over the last 130 years and found Northern Hemisphere winter surface temperatures and associated North Atlantic Oscillation (NAO) variability are correlated with Energetic Electron Precipitation. Although this EEP-NOx is typically considered a solar variable related to sunspot activity, as mentioned earlier, there’s a trend in this EEP-NOx that doesn’t fit solar or geomagnetic activity which may very well be from ground based VLF transmitters.
The same spiraling plasma waves induced by transmitters in the ionosphere and magnetosphere have also been observed flowing UP the solar wind toward the sun and into its convective region. This suggests a possible connection between our broadcast transmitters on a global scale and sunspot activity. If this is true, then it’s possible the same process that allows VLF transmitters to affect climate temperatures through Transmitter Induced Ozone Depletion may have also been affecting dynamics in our solar-terrestrial connection as early as the 1920’s, or 100 years ago leading up to solar cycle 19 in 1958, the largest unpredicted solar cycle anomaly in historic record.
[Figure 12: In the 1930s, radio station WLW was America’s one and only AM radio “Super Station” - its 500kW transmitter caused strange anomalies to occur around the transmitter site.]
[Figure 4: ‘Holes’ form in the ionosphere above VLF transmitters allowing signals to escape into the upper atmosphere fueling changes in upper atmospheric chemistry]
Broadcast Theory of Climate Change - Transmitter Induced Ozone Depletion and the Early Twentieth Century Warming period
Featured in Nexus Magazin (Germany) - August 2020
[Figure 1: Global Warming started around 1910, which began the Early Twentieth Century Warming (ETCW) period when industrial countries built powerful networks of broadcast stations.]
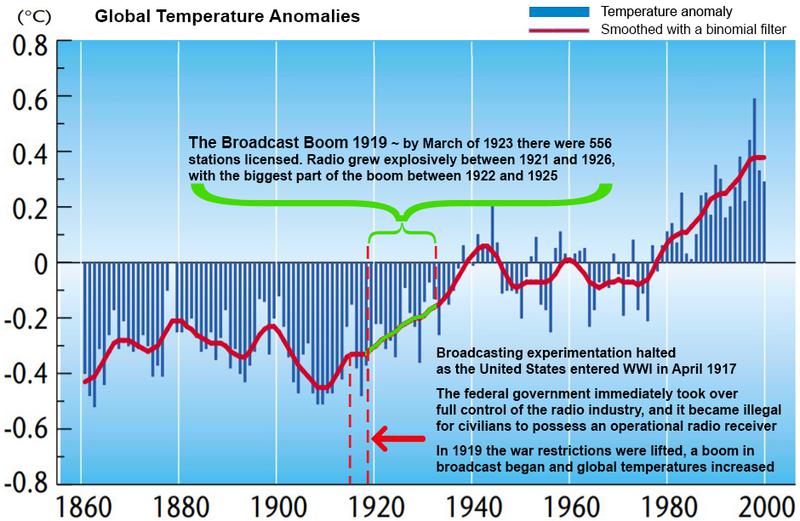
During WWI nearly all commercial and civilian broadcasting equipment was confiscated, and global temperature stalled, only to rise again with the broadcast boom of the early 20’s. I realized that at every point our historic use of broadcast energy shifted on a global scale - our global temperature shifted!
Digging deeper, I discovered there’s an energetic pathway for broadcast energy to stimulate a known ozone depletion mechanism in the upper atmosphere. The explanation for transmitter induced ozone depletion was tucked into niche scientific journals and some of the world's leading physicists had already pointed this out saying the public should be concerned. But the public didn’t know!
So I began collecting anything and everything on this little known hypothesis called “transmitter induced ozone depletion” - and my journey of what’s now become Broadcast Theory of Climate Change began.
I make no claims other than to share a hypothesis made by the cutting edge physicists whose research I share and quote. By the time you’re done reading this, I’ve no doubt you’ll be asking the same questions I and other physicists are. Before we get to Broadcast Theory and how our broadcast technology might have impacted historical climate we need to go over the basic mechanism of Transmitter Induced Ozone Depletion and its possible impacts on climate dynamics.
What is Transmitter Induced Ozone Depletion and TIPER-NOx?
First of all, it’s important to keep in mind that since regular broadcasts began in 1910 with Low and Very Low Frequencies, transmissions have increased in frequency and usage on a global scale to the point that we don’t actually know what “natural” looks like.
An article titled, “Radio waves from Earth clear out space radiation” came out in 2008 in NewScientist magazine saying the same Very Low Frequency (VLF) radio waves and long wavelengths used to penetrate seawater in submarine communications also make it far out into the magnetosphere where they affect trapped particle populations.
The article goes on to say that because high powered VLF radio transmitters have been used since at least the 1920’s in telegraph and submarine communications, we’ve never actually observed the radiation belts as they are naturally, as the belts’ existence was only confirmed in 1958 by the first American satellite, Explorer 1.
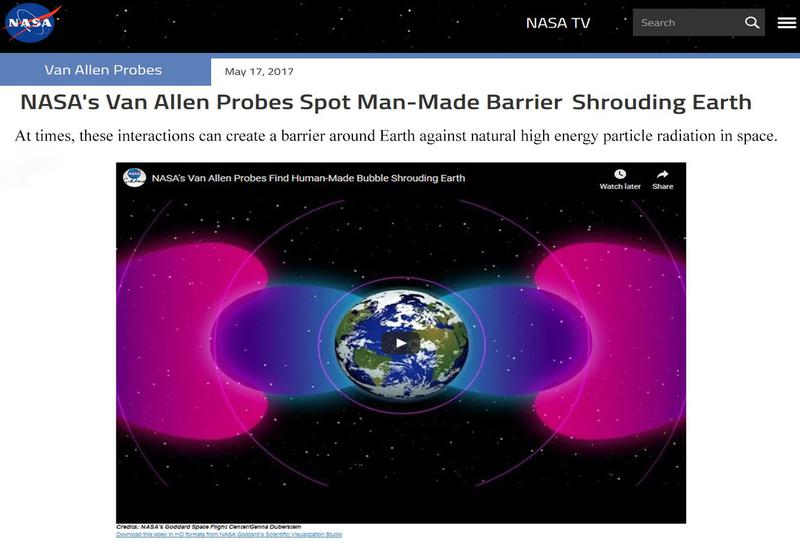
In 2012 two heavily shielded robotic probes were launched to study the Van Allen radiation belts called the Van Allen Probes (VAP). The Van Allen radiation belts are two donut-shaped electromagnetic rings of charged particles that surround the Earth, held in place by the planet’s magnetic field. With the VAP mission they discovered some of these ground based high powered VLF Transmitters had not only cleared some of the radiation belt particle population, but they’d essentially created a bubble of electromagnetic energy surrounding the planet. (see Figure 2)
[Figure 2: The artificial bubble around our planet created by VLF transmitters. It was discovered during the VAP mission.]
Scientists like Dan Baker, director of the University of Colorado’s Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics in Boulder, say the edge of this artificial bubble lines up almost exactly with the inside of the outer edge of the Van Allen belts, suggesting VLF waves deflect solar radiation particles. According to satellite data, the edge of the radiation belt is much further from Earth now than it was in the 1960s, when humans sent fewer VLF transmissions. Dan Baker suspects that if VLF wasn’t around, the radiation belts would hover closer to Earth. In 2017, NASA made a web page and video describing this VLF Transmitter induced bubble based on a paper called ‘Anthropogenic Space Weather’.
As VLF waves push away solar particles and form this bubble; they also clear out electrons trapped in the magnetosphere which then precipitate or rain down into the upper atmosphere. The process is called TIPER: Transmitter Induced Precipitation of Electron Radiation. Detailed by the Stanford University VLF Group these “killer electrons”, as they call them, can damage the sensitive electronics of satellites and prove a health risk to astronauts travelling through the radiation belt and regions of high electron flux.
Early on VLF radio waves were recognized as useful in communicating over long distances because such low frequency radio waves would travel horizontally across the ground bouncing up and down between the conductive ionosphere and the Earth in a zigzag path. Typically the ionosphere would reflect the radio waves so they don’t escape into space and can travel 5,000 to 20,000 km.. however it was later discovered during WWI that some of these radio waves were indeed leaking beyond the ionosphere and into the magnetosphere. These radio wave signals would rise and fall along magnetic field lines in the magnetosphere as discrete packets of plasma waves called “whistlers”.
“One of the first observed effects of space weather on technology occurred during WWI when radio controllers heard dispersed plasma waves called “whistlers” characterized by a descending tone in the VLF radio wave spectrum and were misidentified as falling bombs.”
Though radio waves traveling through the atmosphere fade as they get further from the transmitter being absorbed by atmospheric molecules - according to what’s known as the “inverse square law” - whistlers in magnetospheric wave guides aren’t absorbed or follow this law. To the contrary: In many cases such as the experimental VLF transmitter at Siple Station in Antarctica show, VLF whistler waves are actually amplified as they travel through the magnetosphere to the opposite hemisphere using as little as one watt.
There are over a dozen of these higher powered VLF transmitters located around the globe, three of them making up 50% of the total VLF wave power that dominates the wave particle interactions of the inner magnetosphere; NWC - Australia, NAA - USA & DHO - Germany. (see Figure 3)
Dr. Jaynes was speaking primarily of EEP-NOx, which is also induced by solar activity. However, that same year (2018) a research paper came out stating there was a long term trend in this Energetic Electron Precipitation that did not match solar or geomagnetic activity
(see Figure 6), and admitted that EEP driving ozone depletion may have actually originated from these ground based VLF transmitters. The hypothesis continues.
In 2005, using the DEMETER microsatellite the North West Cape 1000kW VLF Transmitter was found to enhance the electron flux levels 3,600 times above background levels. Then, in 2012, the American Geophysical Union noted this transmitter was creating the massive signature of a huge horseshoe arc in the ionospheric plasma between the north and south hemispheres.
In 2008, the NWC Transmitter was experimentally observed producing ~430 times more Medium Energy Electron Precipitation or MEE above background levels. Using the latest climate modeling has also shown MEE can have significant effects in long term ozone variability, with up to ~20% depletion of polar mesospheric ozone molecules that block ~90% of solar radiation entering our climate system!
Michel Parrot, the lead scientist of the DEMETER mission for the French National Space Agency, said VLF frequencies between 10 and 20 kHz from ground-based transmitters (used for radio-navigation and communications) caused ionospheric heating, turbulence, and particle precipitation. HF frequencies used by broadcasting stations heat the ionosphere, which changes its temperature and density.
He further stated how the transmitter-induced change and dissipation of plasma waves in the ionosphere may participate in the global warming of the Earth. That the precipitation of energetic electrons by man-made waves may trigger lightning discharges, which are an additional source of Nitric Oxide (NOx) that affects the concentration of ozone in the atmosphere which contributes to the greenhouse effect.
Ozone is a sensitive but profoundly important molecule. The reduction of stratospheric ozone allows more solar energy deeper into the climate system which reflects off the surface as Long Wave InfraRed radiation. This InfraRed radiation heats the surface, ocean water and atmosphere along with Green House Gases (GHG) such as CO2, Ozone and water evaporated from the ocean’s surface. Ozone is composed of three oxygen atoms (O3) which readily react with electrons from other molecules, including Ozone Depleting Substances (ODS) such as Chloroflorocarbons (CFCs). For this reason an international treaty called the Montreal Protocol was created to ban the use of CFCs.
Ozone is formed by solar UV and vulnerable to Nitrogen / Hydrogen Oxides present in both the upper as well as the lower atmosphere where ground level ozone forms and acts as a GHG. It’s photochemically created at the equator and transported to the poles via zonal winds and atmospheric dynamics. The altitude at which ozone molecules are created and destroyed are strongly influenced on the electronegativity of the environment where these chemicals react. When transmitters stimulate ion outflows in polar regions and increase the density of ions and electrons, you change the electronegativity and the hydrodynamic processes of ozone are disrupted, which alters the phases of O3 equilibrium and throws its protective effects out of balance.
The old idea that ozone has nothing to do with climate change was overturned in 2019 with discovery of a feedback loop between stratospheric ozone loss and climate change in the Southern Hemisphere.
Though they call the Montreal Protocol a success story, in February of 2020, NASA said the Arctic polar cap ozone was the lowest value in the historic record, showing far more dramatic ozone depletion than the last major Arctic ozone depletion anomaly in 2011. Reports of lower stratospheric ozone depletion continue above populated cities, at the equator, South Africa and the UK! Then months after the largest ozone hole formed over the Arctic, a research paper came out saying ODS weren't as significant in ozone depletion as previously thought.
Russian scientists with the Arctic and Antarctic Research Institute Saint-Petersburg have discovered that the hottest region of climate warming in the Southern Hemisphere has been found to coincide with a stable maximum of EEP (E > 1MeV). These particles may penetrate as low as 20 - 40km and they say it’s quite sufficient to supply input of thermal energy capable of warming the regional atmosphere.
In 2018, the Chinese CSES satellite flew over the central Pacific Ocean
and observed a large region of enhanced Energetic Electron Precipitation.
This EEP was induced by the Australian NWC Transmitter located over a
region of warmer than normal water influential in the El Nino Southern
Oscillation (ENSO). (see Figure 7)
ENSO is an irregularly periodic variation in winds and sea surface
temperatures over the tropical eastern Pacific Ocean, affecting the
tropics and subtropical climate, and was recently found to be dependent
on stratospheric ozone which can affect zonal winds by the amount of
solar UV that makes it through the ozone layer, warming regional areas
of the atmosphere.
CSES satellite also observed radio waves from the NWC Transmitter in the
Southern hemisphere ducting through the magnetosphere to a similar point
in the opposite, northern hemisphere, where it was reacting with PowerLine
Radiation from the Chinese power grid which also creates whistlers in the
magnetosphere.
If the NWC Transmitter in Australia has been experimentally shown to
produce ~430 times more Medium Energy EEP.. and other research
suggests MEE can reduce polar mesospheric ozone ~20% - then it's
worth considering that the MEE created by the NWC transmitter might
also be having a significant effect on ozone variability - especially if we're
witnessing a warm spot in the ocean right under the MEE anomaly.
In December 2019, the recurrence of another anomaly - a massive,
warmer-than-normal pool of water, first discovered in 2013 - formed in
the Pacific Ocean off the Washington coast called ‘The Blob’. Six years
earlier, satellites observed an enhancement of Energetic Electron
Precipitation in this area created by interactions between two VLF
transmitters; one north of Seattle and the other in Hawaii.
We can dismiss oceanic warm spots as completely natural, but given
the complex interplay of upper atmospheric ozone and Transmitter
Induced Electron Precipitation, we don’t actually know what
“natural” is anymore.
[Figure 8: Zapping the ionosphere with radio waves at the ionospheres’ own natural frequency will cause spiraling plasma waves to flow along magnetic field lines toward the poles causing ion outflow that may lead to ozone depletion]
Gyro~frequencies aka: The Bailey Effect
The Gyro-frequencies have a range between 630kHz to 1630kHz coinciding with most of the AM broadcast band. The actual gyro frequency in an area depends on the geographical location and the height of the ionosphere, and broadcasters typically avoid the local gyro frequency because its ionospheric absorption gives terrible signal reception. But there are factors that either cannot be influenced or are not taken care of: geomagnetic storms, for example, cause fluctuations in ionospheric height which can bring nearby stations into their local gyrofrequency range - and radio waves from powerful transmitters that cover a huge area can “hit” gyro frequencies from other locations.
This gyro-frequency phenomenon was first explored by V. A. Bailey in the mid 30’s when it first became known as The Bailey Effect. It was through a set of early radio propagation experiments using local radio towers that Bailey discovered this effect and in 1937. Based on his experiments Bailey predicted it would only take 1 - 2kW (1000 - 2000 watts) to stimulate this effect whereby the radio waves would cause heating in the ionosphere and boost other VLF signals passing through the heated region 4 - 10 times.
In 1946, it was experimentally verified only 400 - 500 watts would cause this effect. Currently AM broadcast is limited to 50,000 watts.. this is over 100 times the power output needed to stimulate these non-linear plasma effects that magnify other local signals by 400 ~ 1000 times! In 1961 a highly classified 1.45MHz transmitter was built in Moscow, Russia to test the Bailey effect on artificial airglow.
To understand more about how the AM broadcast band could stimulate unique upper atmospheric processes, we have to look back at how these frequencies were used in the evolution of our broadcast history to understand the potential of its chronological effects on the atmosphere.
Broadcast History:
It all began Christmas eve of 1909 with the first regular radio broadcast sent out upon the air waves. The pioneering work of great minds like Nikola Tesla, Thomas Edison and Marconi came to a growing civilization. The first broadcast tower was built in San Jose California by an electronics instructor named Charles Herrold. The station used spark gap technology and went by “San Jose Calling” which eventually became KCBS in San Francisco. Charles began by designing an omni directional antenna which he mounted on many rooftops in San Jose to help the radio signal spread in all directions.
The first experimental antenna designs were large and complex using a ‘flattop’ antenna design, which propagates skywave far better (x2 ~ 4) than the ‘vertical’ antennas we developed later in the 30’s. Early skywave caused radio signals to bounce back from the ionosphere creating a great deal of interference and upset broadcasters. The same “flattop” design is used by theHAARP scientific transmitter in Alaska for its effectiveness in ionosphere frequency pumping and experimental excitation of plasma wave phenomena such as those seen in the EEP-NOx process.
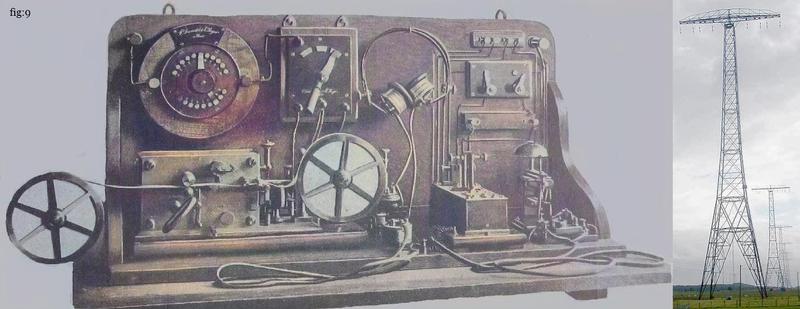
Around 1910 industrial countries began building powerful networks of transoceanic LongWave radiotelegraphy stations to communicate with other countries using Morse code. (see Figure 9)
[Figure 9. Left: Commercial radiotelegraphy receiver from the first decade of the 20th century. Right: Grimeton Radio Station: in southern Sweden, an early longwave transatlantic wireless telegraphy station. From the 1920s through the 1940s it transmitted telegram traffic by Morse code to North America and other countries.]
A quote from an article on our broadcast history shows the amount of power these early stations generated using powerful spark gap technology:
“Huge spark stations of tremendous power were developed, using giant antennas. By later standards these early stations were absurdly overpowered – in fact they were so powerful that their signals were probably traveling around the world more than once. However receivers were so insensitive, these transmitting behemoths were needed in order to insure quality service.”
After the Titanic sank in 1912 - and by the end of World War I - the United States military began use of Very Low Frequency radio transmissions (VLF; 3–30 kHz) radiated from large shore-based antenna complexes and on ships for safety reasons.
As amateurs were beginning to explore the technology, it began to grow. However during the war the government soldiers confiscated all transmitting and receiving equipment. The only civilian station that was allowed to continue was Westinghouse.
Early experiments also showed VLF could penetrate seawater, a fact realized by the British Royal Navy during World War I. Through a series of experiments at VLF frequencies, the US Naval Research Laboratory refined underwater communications. Those upgrades led to the current US Navy VLF communications network, and other countries followed suit.
1919 - 1925 - The Broadcast Boom
With the end of WWI and broadcasting restrictions the broadcast boom of the early 20’s began and by 1920, human voices and strains of music were heard regularly over the airwaves. In 1921 there was 1 regular broadcast station and by March of 1923 there were 556 stations licensed. Radio grew explosively between 1921 and 1926, with the biggest part of the boom between 1922 and 1925. Newspapers and department stores started broadcasting and advertising. The Netherlands, Argentina and other countries followed suit as it began to spread across the globe.
As broadcast took off, the global temperature of our climate soared faster and higher as we can see in the global temperature anomalies graph during what became known as the Early Twentieth Century Warming (ETCW) period between 1910 - 1945, with a temperature increase of 0.37 K between 1925 - 1944. (see Figure 10)
[Figure 10: When WWI began nearly all civilian broadcasting was restricted and the global temperature stalled. When wartime restrictions ended the broadcast boom saw global temperatures rise]
The first experimental antenna designs were large and complex using a ‘flattop’ antenna design, and as higher frequencies were explored a new phenomenon was discovered: skywave. Skywave signals bounce back from the ionosphere creating a great deal of interference over great distances sometimes resulting in hearing more than one program at the same time. Early frequency control was bad and changed as the antennas swung in the wind and by 1923, it was clear that a major overhaul of the broadcasting service was needed.
The continued expansion brought further adjustments, regulations and issues that the government had to sort out. By 1925 there were 536 broadcasting station providers for an estimated half million radio receivers, 200 of which fell in the gyrofrequency range with enough power (400/500 watts) to stimulate the Bailey Effect that can boost passing VLF signals 4 - 10 times.
1925 - 1945 - Broadcast Chaos & Experimentation
In 1927 a torrent of new stations and frequency changes flooded the airwaves and an increase in interference was felt nationwide. As chaos spread over the airwaves stations paired up to intentionally jam the airwaves so as to force the creation of a new regulatory structure amidst the pleas from radio stations everywhere.
In 1928 a new structure for the broadcasting system was defined and the number of stations were reduced to 585. Setting aside frequencies for Canadian and Clear Channel use permitted usage up to 50 kilowatts. This reallocation finally “brought order out of chaos” and nearly seventy years later this historic work still provides the underpinning for the AM broadcast band.
In the years following three major broadcasting experiments were explored that helped us realize the upper boundaries of what was possible and how turbulent ionospheric processes may have been fueled by broadcast technology: AM APEX aka “Skycraper Radio”, America’s first “Superstation” WLW700 Cincinnati, and the rise of FM - Frequency Modulation.
1932 - 1941 AM-APEX “Skyscraper Radio” [25 - 42MHz]
The FCC encouraged broadcasters to experiment with “ultra high frequencies” above 20 MHz and in 1934 regular broadcasts began in New York. Then in 1937, the FCC decided to make official a high-frequency broadcast band in which every channel had four times the width of a typical AM channel, so there was less interference. It could accommodate a better-sounding — but still AM — signal at what was then considered the upper limits of practical radio technology, a form of “Ultra Short Wave” named “Apex” because of their high frequencies and high antenna locations.
By 1939, there were Apex station stations operating in 34 cities in 22 states and they could operate up to 1,000 watts on frequencies at 25-26 MHz and 42 MHz. However, not much was known about the propagation characteristics at 25-40 MHz in the early 1930’s, and as today’s ham radio operators know very well, propagation conditions on the frequencies used by the Apex stations vary tremendously over the eleven year sunspot cycle. When the first Apex experiments began in 1932, the sun was just coming out of a sunspot minimum, so the new stations probably experienced mostly interference-free coverage during their first few years of operation. But sunspots were at their peak in 1936, and suddenly the experimental Apex stations were being heard ..all around the globe!
This was a huge problem and later it was discovered by the War Department in 1945 that 42MHz was particularly effective at causing interference with skywaves that bounced off the ionosphere.
With these issues and the discovery of FM.. AM Apex stations shut down in 1941 and during this time the global temperature began to slow its meteoric rise of the ETCW period. (see Figure 11)
[Figure 14: 1946 & 1998 - The two years with the largest decommissioning of VLF transmitters saw a hiatus in global temperature increases]
The CO2-driven Climate Change narrative says that we are in a runaway warming trend, however since 1910 at the beginning of the Early Twentieth Century Warming period, even though CO2 emissions have increased, global temperatures have not. Some of the mainstream data presented don't accurately represent these periods of hiatus, and fuel basic assumptions that may not be accurate. So know your sources and choose wisely. Climate Change may not be as bad as we think it is, but even if regional micro-climates are anthropogenically altered, the lives who depend on those are no less affected.
Could it be the rise of FM and VLF broadcasting frequencies in the 70’s began to saturate the ionosphere.. further fueling upper atmospheric ozone depletion processes and the subsequent rise in global temperature? Could it be that the decommissioning of VLF Transmitters in 1998 stalled transmitter induced ozone depletion and its effects on the climate system?
Summary of Broadcast Theory Correlations & Questions:
These experiments and innovations are examples of dynamic shifts in our evolving use of broadcasting technology in the early days of radio.. a time when our airwaves weren’t nearly as saturated by higher frequencies. The FCC’s bandwidth reallocation efforts to cope with increasing demand and frequency usage, the end of AM Apex and WLW, along with the invention of FM, Television and the decommissioning of VLF transmitters during the 40’s, resulted in what became the largest shift in our historic use of broadcast technology since it first began around 1910.
Let’s review the main arguments. Broadcast Theory says:
- Some, if not all, but at least the most powerful broadcasting stations using VLF frequencies or frequencies near the gyro frequency in the AM broadcast band generate plasma waves in the upper atmosphere.
- These plasma waves, fuelled by other processes, travel to polar regions.
- There they cause magnetospheric electrons to slip down into the polar vortex - a mechanism called TIPER.
- This possibly increases NOx via a mechanism called EEP-NOx.
- Those additional NOx react with the ozone in the stratosphere which is chewed away.
- The depletion of ozone allows more solar radiation into the climate system which leads to a continuing warming trend.
The question Broadcast Theory asks is:
Did the shifts in our historic use of broadcast involve the known hypothesis of Transmitter Induced Ozone Depletion and have an effect on the Early Twentieth Century Warming period and the Great Winter of 1946/47? (see Figure 15)
[Figure 15: Broadcast Theory asks if our historic use of broadcast influenced the Early Twentieth Century Warming period through the Transmitter Induced Ozone Depletion mechanism.]
If Transmitter Induced Ozone Depletion decreased in the 40’s, maybe the ozone layer rebounded. A thicker stratospheric ozone layer blocks more solar radiation from entering the climate system and with less solar radiation the climate system went through a 5 year cooling trend as the global temperature decreased beginning with the Great Winter of 1946/47.
This isn't just about ozone ‘depletion’, it’s about a two way variable that may have effects on long term temperature trends both increasing and decreasing in both hemispheres, a regional dynamic that translates to a global effect because similar transmitters are used in the US, Europe, Australia and other parts of the world.
These VLF waves have formed a bubble around the planet that might not only stimulate ozone depletion, but according to NASA, are capable of blocking solar particles from Earth. Scientists refer to it as an ‘impenetrable barrier’ and are still trying to understand the dynamics of the wave particle acceleration and losses to the upper atmosphere.
During geomagnetic storms shortwave radio and frequencies near their local gyro-frequency in the AM broadcast band and signals from lightning leak through holes in the ionosphere created above VLF transmitter sites, potentially fueling EEP-NOx in an anthropogenic amplification process that gets lost in the noise of natural geomagnetic storms. If true we might consider limiting or even ban AM channels even near their local gyrofrequency for not only reception quality and interference, but also its potential effects on the environment.
Though many people point fingers at H.A.A.R.P as the bad guy, it’s important to realize that unlike the transient experiments done occasionally with HAARP beginning in 1993, VLF Transmitters had been broadcasting continually - near non-stop ALL THE TIME since at least the 1920’s! The HAARP transmitter, though powerful, is a small drop in a very deep bucked when you consider the total output of man-made RF into the atmosphere. So before we go pointing fingers at one scientific transmitter.. perhaps we should also take a look in our own backyard. Not to say HAARP isn’t a concern, but if we are looking at *long term* climate impacts induced by broadcast transmitters we need to look at transmitters that are ON *continuously* and trends in their use.
I don’t know how significant broadcast may be to the climate system, but there's plenty of evidence to make it worth considering and some of the world's leading physicists say we should be concerned. The pathway of energy that allows broadcast transmitters to stimulate ozone depletion is there and so is the input.
Broadcast technology continues to evolve and in recent years we have added cellular and 5G satellite technology to our broadcast spectrum. Maybe history and broadcast theory urges us to be more cautious with the energy we add to the global electric circuit - since it may have detrimental effects on our climate and environment.
So welcome to Broadcast Theory ~ a high resolution analysis of global temperature trends and Transmitter Induced Ozone Depletion in the context of our historic use of broadcast technology and the Early Twentieth Century Warming period. Perhaps one day we'll look back to this time of climate struggle and see how our persistence to understand the world around us eventually paid off. Not only might we stabilize our climate as best we can, but perhaps we may go on to use this understanding to terraform other worlds.
About the author:
Ethan Clark began researching Transmitter Induced Ozone Depletion in 2006/7 after doing research for a CO2-driven Climate Change website and stumbling upon this hypothesis physicists have been pondering since the 70’s. He compiled research on this mechanism, built the Broadcast Theory website, created a number of videos to help people understand TIPER-NOx and continues to share insight on how the mechanism of Transmitter Induced Ozone Depletion potentially interacts with climate dynamics.
Some of his presentation material on EEP-NOx was used by Dr. Allison Jaynes in her 2018 National Academy of Sciences presentation on ‘Cutting Edge Radiation Belt Research’. He has a Material Science degree in NanoEngineering, is HAM Technician Class certified and volunteered with the Seattle Police Auxiliary Communication Services while continuing to do Broadcast Theory research and connecting with scientists around the world on the potential impact broadcast technology may have with our ever changing environment.
If interested in discussing the topic you can contact him at: broadcasttheory@gmail.com
Follow his latest research on Face Book: https://www.facebook.com/ethan.clark.96930/
Visit the Broadcast Theory website: Www.BroadcastTheory.com ~ #tiperNOx
WMO Global Temperature Anomalies Graph:
Zombie Satellites, Killer Electrons, Ozone Depletion and Climate Change! ~ by Craig Rodger at the Uni of Otago
Figure Box 1: Transmitters create spiraling plasma waves and ion outflows that alter polar region particle densities. Those waves have been observed flowing to the sun. Are they affecting the sunspot activity, since it follows temperature trends in climate?
References: Click to Enlarge
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
Radiation Belt Remidiation ~ Transmitter Induced Ozone Depletion!
Top Scientists say using radio waves to alter radiation belts may deplete ozone
“Three space experiments—one now in orbit and two being readied for launch in 2021—aim to gather data on how to drain high-energy electrons trapped by Earth’s magnetic field in radiation belts encircling the planet.
The process, called radiation belt remediation (RBR), already happens naturally, when radio waves from deep space or from Earth—our own radio chatter, for example, or emissions from lightning—knock electrons trapped in Earth’s Van Allen radiation belts into the upper atmosphere, where they quickly shed energy, often triggering aurorae.
A full-scale space cleanup might dump as much energy into the upper atmosphere as the geomagnetic storms caused by the Sun’s occasional eruptions. Like them, it could disrupt airplane navigation and communication.
👉And it would spawn heaps of nitrogen oxides (NOx) and hydrogen oxides (HOx), which could eat away at the stratospheric ozone layer. 👈
“We don’t know how great the effect would be,” says Allison Jaynes, a space physicist at the University of Iowa”
~ ~ ~
Broadcast Theory of Climate Change
Www.BroadcastTheory.com ~ #tiperNOx
What was once thought purely a solar climate variable.. may be influenced anthropogenically!
Sun provides the heat.. ozone is the valve.
"The Energetic Electron Precipitation (EEP) events are associated mainly with high-velocity solar wind fluxes and are often observed during the decaying phase of the 11-year solar cycle.
A long-term growing trend that does not correlate with the parameters of solar and geomagnetic activity has been observed in the occurrence rate of EEP precipitation.
👉This trend could be due to the effect of ground-based VLF transmitters📡on the wave activity of the magnetosphere.👈
The part played by EEP precipitating magnetospheric electrons in atmospheric chemical reactions responsible for the dynamics of the ozone content and changes in temperature in the stratosphere and mesosphere is also poorly understood"
~ ~ ~
Broadcast Theory of Climate Change
Www.BroadcastTheory.com ~ #tiperNOx
This is an AMAZING presentation by Craig Rodger at the University of Otago. He's the most zany animated scientist who will leave you entertained as well as informed. 🧐
Rarely does a scientific presentation make me laugh and even more rarely does one bring me tears because the subject is so near and dear to my passion.
This is a remix of two presentations he did on the subject of ‘Killer Electrons’ which is really a catchy term scientists use for Energetic Electron Precipitation aka: EEP which as he explains is an upper atmospheric phenomenon that can have a dynamic effect on stratospheric ozone losses and climate temperatures.
The first one done in 2014 is the funnest to watch, though his 2016 presentation added new data regarding *long term* EEP-NOx effects on ozone variability.
~ ~ (Video RemiX ~32min)
U of Otago: Zombie Satellites, AARDDVARK Radio, Killer Electrons and Space Physics: [https://youtu.be/zuTFQ0nZ4do]
~
Space Talk at SANSA: Zombie Satellites, Killer Electrons and Physics in Space: [https://youtu.be/kzQsq9RkYFQ]
~
LASP UCBoulder: Zombie Satellites, Killer Electrons, and Physics in Space—AARDDVARK Radio research: [https://youtu.be/_qjk8RRzyrc]
~ ~ ~
Broadcast Theory of Climate Change
Www.BroadcastTheory.com ~ #tiperNOx
Long-Term Evolution of the Occurrence Rate of Magnetospheric Electron Precipitation into the Earth’s Atmosphere:! ~