Studies of Electromagnetic Radiation in Space
Highlights
Ionosphere disturbances generated by different natural processes and by human activity in Earth plasma environment
“We can observe parallel to direct radiation also in the emissions of ionos-pheric plasma triggered by transmitters of electromagnetic waves located around the world. Human activity can be seen on the recorded spectra as separated peaks, growing of the whole background of plasma emission or enhanced broadband emissions in the whole observed frequency range (fig. 17.4).”
“The permanently pumped electromagnetic waves to the ionosphere by the system of broadcasting
stations can disturb the nearest space environment. Thus this activity can create in the topside ionosphere local Langmuir turbulence or ion-acoustic turbulence. However theoretical assumptions show that the generation of ion-acoustic turbulence is far more effective. The scattering of super-thermal electrons on ion-acoustic or Langmuir turbulence is proposed as a mechanism of generation of broad-band HF emissions. The HF diagnostics, performed on the low orbiting satellite, detected an enhancement of radiation particularly over the Euro-Asia region. HF emission in the topside ionosphere is more intense over the area correlated with outer radiation belts. It is prominent on the Eastern Hemisphere i.e. some longitudinal effect is manifested. The observed effect is markedly visible, and is stronger in the night-side ionosphere. Strong geomagnetic disturbances can broaden the area of observed intensification of HF noises in comparison with quiet time, but the intensity of the observed enhancement is not affected by eomagnetic disturbances” (Rothkaehl and Klos, 2002) (fig. 17.5)
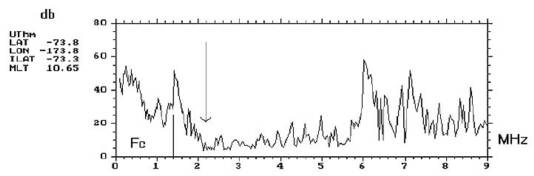
Fig. 17.4. The example of typical single HF spectrum detected on board the Coronas-I satellite, the line marks
the local electron gyrofrequency at the satellite altitude and the arrow the cut-off of local plasma emission UHR
(Upper Hybrid Resonance). The well pronounced emission for frequencies larger than UHR are related to human activity, mainly broadcasting station activity.
HANNA ROTHKAEHL (1), NATALY IZOHKINA (2), IGOR PRUTENSKY (2), SERGEY PULINETS (2) (3),
MICHEL PARROT (4), GEORGYI LIZUNOV (5), JAN BL⁄ ECKI (1) and IWONA STANISL⁄ AWSKA (1)
Source
Back
Wave-particles interaction in radiation belt region Slideshow
http://slideplayer.com/slide/2375613/
Click to Enlarge